It’s a startling reality for dog owners that choking incidents are all too common among dogs. Accidents can occur unexpectedly, emphasizing the importance of understanding how to identify and address potential choking hazards. In this blog, we’ll delve into the frequent items dogs swallow, explore the underlying reasons for their curious behavior and discuss vital first aid techniques for handling choking emergencies. Additionally, we’ll uncover proactive measures such as securing our homes, choosing safe toys and teaching essential commands to mitigate the risk of choking incidents. Learn how to navigate through these crucial aspects of canine safety and well-being.
Understanding the Risk
Common Items Dogs Swallow
Dogs are naturally curious creatures, and their inquisitive nature often leads them to investigate and sometimes swallow items they shouldn’t. Among the most commonly swallowed objects are chew toys and children’s toys, which can break into small, ingestible parts. Bones, particularly those that are cooked or made of rawhide, can splinter and cause severe internal damage. Gristle, which is difficult to chew, is actually one of the most common things dogs choke on each year. Rocks are another common issue, as some dogs, especially puppies, seem obsessed with them. If swallowed, rocks can become lodged in the throat and cause total obstruction.
Household items like socks, coins and other small objects frequently find their way into a dog’s mouth, posing significant risks if ingested. Even certain food items such as grapes and chocolate are not only choking hazards but are also toxic to dogs. Grapes can cause kidney failure, and chocolate contains theobromine, which is harmful to canine health.

Why Dogs Swallow Objects
Dogs often swallow objects due to a combination of curiosity, playfulness and natural scavenging behavior. Their curiosity drives them to explore their environment with their mouths, leading them to chew on and sometimes ingest various items. Playfulness also plays a significant role, as dogs might get excited during play and accidentally swallow parts of toys or other objects. Additionally, their natural scavenging behavior, inherited from their wild ancestors, compels them to forage and eat whatever they find, regardless of whether it’s food.
Dogs that are aggressive chewers are particularly prone to swallowing objects due to their intense chewing habits. These dogs tend to rip apart the items they are chewing with great force and speed, breaking them into smaller, often sharp, fragments. In their eagerness and excitement, they may swallow these pieces quickly without fully chewing them. Aggressive chewers often lack the patience to carefully chew and explore objects.
Recognizing the Signs of Choking
Immediate Signs
When a dog is choking, recognizing the immediate signs can be crucial for your dog’s life. One of the most common indicators is gagging or retching, as the dog instinctively tries to dislodge the object obstructing its airway. This may be accompanied by heaving motions and sounds of distress. Coughing is another frequent symptom, which often occurs as the dog attempts to clear its throat. This coughing might be forceful and persistent, differing from normal coughing due to the urgency and intensity.
Difficulty breathing is a particularly alarming sign. A choking dog may take rapid, shallow breaths, or you might notice it struggling to breathe, with its chest and abdomen visibly heaving. The dog’s gums might also appear pale or bluish due to a lack of oxygen. A dog in distress might paw frantically at its mouth, trying to remove the obstruction. This behavior, combined with anxious pacing or frantic movements, highlights the severity of the situation.
Signs of a Swallowed Object
One of the first indicators is excessive drooling, as the dog’s body reacts to the foreign object in its digestive tract. This drooling may be accompanied by frequent attempts to swallow or lick their lips. Vomiting is another common sign; the dog may attempt to expel the object naturally, leading to repeated bouts of vomiting or dry heaving.
A noticeable lack of appetite can also signal that something is wrong. The dog may refuse to eat due to discomfort or a feeling of fullness caused by the obstruction. Even favorite treats might be ignored, indicating a deeper issue. Also, abdominal pain often accompanies a swallowed object. You might observe your dog showing signs of distress when its abdomen is touched, such as whimpering, growling or attempting to move away. The dog may also adopt a hunched posture or lie down more frequently to alleviate the discomfort. In some cases, you might notice changes in bowel movements, such as constipation or diarrhea, which can further indicate an internal issue.
First Aid for a Choking Dog
Stay Calm and Check Their Mouths
If you find yourself in the frightening situation of a choking dog, it’s crucial to stay calm. Your composed demeanor will help reassure your pet and enable you to act quickly and effectively. Begin by carefully checking your dog’s mouth for any visible obstructions. Gently open its mouth, being mindful of not causing further injury, and inspect for any foreign objects that may be blocking the airway. If you see something, attempt to remove it using appropriate techniques, such as using your fingers to sweep the object out or performing a modified Heimlich maneuver.
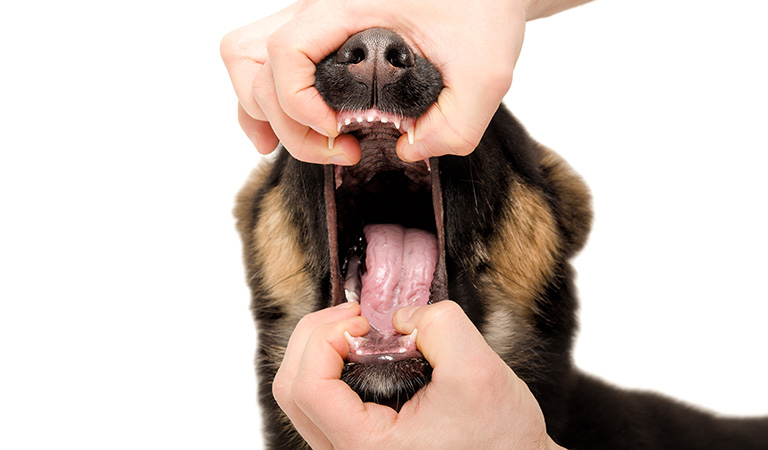

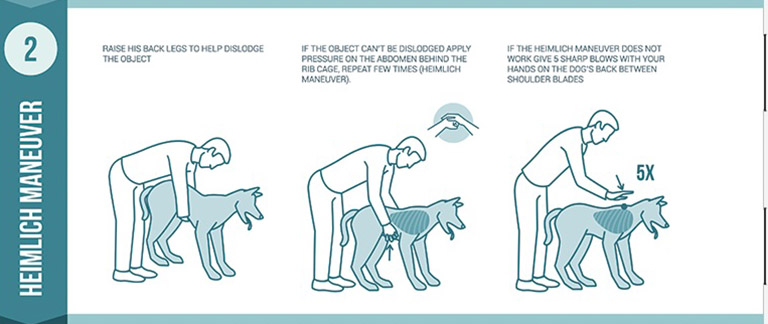
Heimlich Maneuver on Dogs
Small Dogs: To perform the Heimlich maneuver on your small dog, carefully place your small dog on your lap and gently turn them onto their back. Using the palm of your hand, apply firm pressure right beneath the rib cage, pushing inward and upward in a thrusting motion, repeating five times. After each thrust, roll your dog back onto their side and check their mouth for the food or object causing the choking issue. This technique can help dislodge the obstruction and restore your dog’s ability to breathe properly.
Medium and Large Dogs: The Heimlich maneuver can be performed on medium and large dogs whether they are standing or lying down. If your dog is standing, gently wrap your arms around them so that your hands meet at their abdomen. Form a fist with your hands and swiftly push up and forward five times in a thrusting motion. This action should help dislodge the food or object causing the choking. After performing the maneuver, immediately check your dog’s mouth to remove any loose food or objects from the back of their throat to prevent choking or further ingestion.
If your dog is lying on the floor, position one hand on their back and use your other hand to press or squeeze their abdomen upwards and forward toward the spine. This motion aims to create the necessary pressure to expel the obstruction. Once done, carefully examine your dog’s mouth to locate and remove the offending object.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to stop your first aid efforts and seek professional help is critical in a choking emergency. If your dog continues to choke despite your attempts to dislodge the obstruction, it’s essential to act swiftly. Persistent choking, especially if it worsens or shows no signs of improvement, indicates the need for immediate veterinary attention.
Changes in your dog’s color or consciousness level are also red flags that warrant immediate action. If your dog’s gums or tongue turn blue or pale, indicating a lack of oxygen or if they lose consciousness altogether, it’s crucial to act decisively. These are serious signs of a life-threatening emergency, and your dog requires urgent medical attention.
In any of these scenarios, do not hesitate to contact your veterinarian or the nearest emergency animal hospital. Time is of the essence in a choking emergency, and swift professional intervention can make all the difference in your dog’s outcome.
How to Transport Your Choking Dog to the Vet
When transporting your choking dog to the vet, prioritize their safety by handling them gently and avoiding sudden movements. Enlist assistance if needed, especially for larger dogs or navigating obstacles. Remain vigilant for any changes in your dog’s condition during the journey and be prepared to provide first aid if necessary. By remaining calm and ensuring your dog’s comfort during transport, you can help ensure the best possible outcome for your pet.
When Your Dog Swallows Something Harmful
Assess the Situation
The first step when your dog swallows something harmful is to assess the situation carefully. Determine if the object is likely to pass through the digestive system without causing harm, or if it poses an emergency situation. Small, soft items may pass naturally, while sharp or toxic objects require immediate attention.
Immediate Steps
In the event of a harmful ingestion, it’s crucial to remain calm and avoid panicking. Refrain from inducing vomiting unless specifically instructed to do so by your veterinarian, as certain substances or objects can cause further damage if brought back up. Keep your dog calm and still to prevent the object from causing additional distress or complications.
Contact Your Vet
After assessing the situation and ensuring your dog’s immediate safety, promptly contact your veterinarian for further guidance and assistance. Provide detailed information about the ingested object, including its size, composition and any accompanying symptoms your dog may be experiencing. Your vet will advise you on the appropriate course of action, which may include monitoring your dog closely at home, bringing them in for an examination or administering specific treatments or procedures to address the ingestion.

Tips to Prevent Dogs from Choking
Dog-Proofing Your Home to Prevent Choking
Start by keeping small objects out of your dog’s reach, as curious pets may be tempted to investigate and potentially swallow them. Store items such as coins, batteries, small toys and household trinkets in secure cabinets or drawers where your dog cannot access them. Be especially mindful of items that are easily overlooked but pose significant choking hazards, such as rubber bands, hair ties and button batteries.
Appropriate Toys for Dogs
Carefully select and monitor your dog’s toys to ensure they are safe for chewing. Choose toys that are appropriately sized for your dog’s breed and chewing habits, and opt for sturdy, durable materials that are less likely to break into small, ingestible pieces. Regularly inspect your dog’s toys for signs of wear and tear, discarding any damaged or broken items promptly to prevent accidental ingestion.
When it comes to bones, exercise caution and choose appropriate options for your dog’s size and chewing habits. Avoid cooked bones, which can splinter and cause serious internal injuries, and opt for raw bones or specially designed chew toys instead. Monitor your dog closely when they are chewing on bones and remove any small or sharp fragments to prevent choking or digestive issues.

Training Commands for Your Dog to Prevent Choking
Teaching your dog essential commands like “leave it” and “drop it” can play a crucial role in preventing swallowing hazards and reducing the risk of choking incidents. The “leave it” command teaches your dog to refrain from picking up or ingesting potentially harmful objects, while “drop it” instructs them to release items already in their mouth. Consistent training and positive reinforcement can help your dog understand these commands and respond promptly in situations where they encounter choking hazards.
Practice these commands regularly during training sessions and incorporate them into everyday activities, such as walks or playtime. Start with simple exercises using treats or toys as distractions, gradually increasing the level of difficulty as your dog becomes more proficient. Reinforce good behavior with praise and rewards to reinforce the desired actions and encourage compliance.
Dogs Safety and Well-Being
As responsible dog owners, it’s our duty to prioritize the safety and well-being of our canine companions. By understanding the common items dogs swallow, recognizing the signs of choking and knowing how to respond effectively in an emergency, you can ensure prompt intervention and potentially life-saving assistance for our furry friends.
Implementing preventative measures such as dog-proofing your home, selecting appropriate toys and training essential commands can significantly reduce the risk of choking incidents and promote a safe and enriching environment for our dogs to thrive.


